As a seasoned blogger, I’ve delved into various topics, but few are as pressing as the impact of climate change on global agriculture. Climate change isn’t just a distant threat—it’s reshaping the very foundation of how we grow our food. From shifting weather patterns to the rise in extreme events, the effects on agriculture are profound and far-reaching.
In this article, I’ll explore the intricate relationship between climate change and global agriculture. As temperatures rise and weather becomes more unpredictable, farmers worldwide are facing unprecedented challenges. The implications go beyond just crop yields; they extend to food security, economic stability, and even social dynamics. Understanding these complexities is crucial in shaping sustainable practices for the future of our food systems.
Examining the Impact of Climate Change on Global Agriculture
As I delve into the impact of climate change on global agriculture, it’s crucial to understand the direct effects it has on crop yields and the subsequent changes in agricultural practices.
Effects on Crop Yields
Climate change has a direct impact on crop yields worldwide. With rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns, farmers are encountering challenges in maintaining consistent and high yields. Extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves are becoming more frequent, leading to crop failures and reduced productivity.
Changes in Agricultural Practices
In response to the challenges posed by climate change, farmers are adapting their agricultural practices. They are implementing techniques that focus on sustainability and resilience to mitigate the impact of changing environmental conditions. These changes include the adoption of drought-resistant crop varieties, precision agriculture using data and technology, and sustainable water management practices to ensure long-term agricultural productivity.
Regional Impact Analysis
As I delve into the regional effects of climate change on global agriculture, it’s evident that North American farming faces unique challenges. Extreme weather events threaten crop production, with increased temperatures affecting crop yields. Precision agriculture and sustainable practices are crucial for mitigating these impacts in the region.
Impact on North American Farming
In North America, climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture. Higher temperatures lead to changes in growing seasons, impacting crop cultivation. As a result, farmers are adopting precision agriculture methods, such as using data-driven technologies to optimize crop management and resource utilization. Sustainable practices like no-till farming and crop rotation are increasingly employed to enhance resilience against erratic weather patterns.
Effect on Asian Agriculture
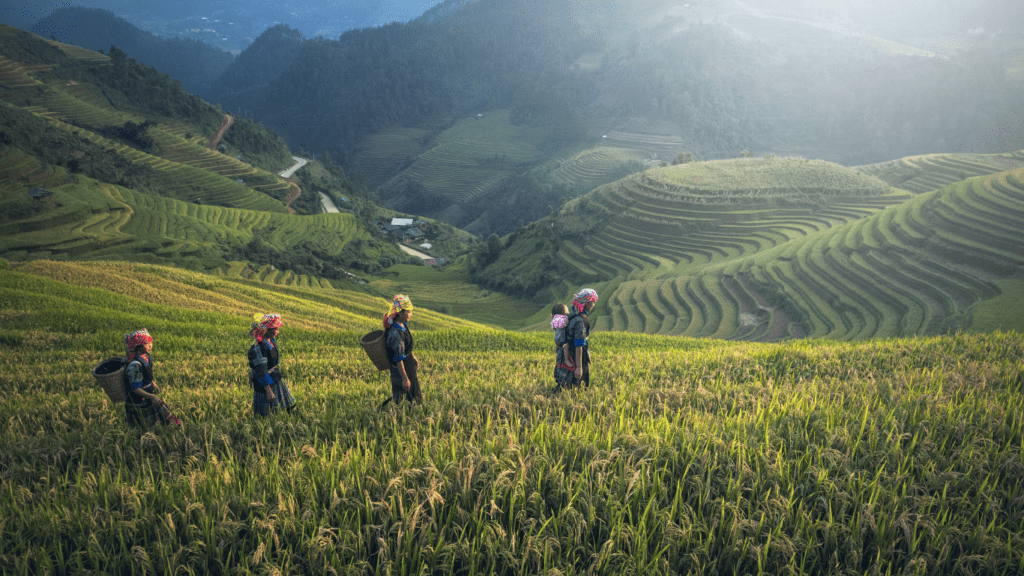

Climate change impacts Asian agriculture profoundly due to the region’s heavy reliance on rain-fed farming. Erratic rainfall patterns and increasing temperatures disrupt crop cycles, resulting in reduced yields and food insecurity. To combat these challenges, farmers in Asia are turning to sustainable water management techniques, like rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation systems. Additionally, the adoption of climate-resilient crop varieties helps improve productivity in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Challenges for African Farmers
African farmers are among the most vulnerable to the effects of climate change on agriculture. Unpredictable weather events, such as prolonged droughts and floods, threaten food production and livelihoods in the region. African farmers are implementing adaptive strategies like agroforestry and conservation agriculture to enhance soil health and water retention. Access to technology and financial support remains crucial in building resilience among African farmers facing these climatic challenges.
Adaptation Strategies and Innovations
In addressing the challenges posed by climate change in agriculture, several adaptation strategies and innovations have emerged to enhance sustainability and productivity. These advancements encompass technological solutions, policy measures, and sustainable practices that aim to mitigate the impact of changing climatic conditions on global food systems.
- Technological Advances in Farming
Technology plays a critical role in revolutionizing farming practices to adapt to climate change. One significant advancement is the development of precision agriculture techniques. This approach utilizes cutting-edge technology such as drones, sensors, and GPS mapping to optimize crop production by precisely managing inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides. Precision agriculture enhances resource efficiency, reduces environmental impact, and improves crop resilience to fluctuating climate conditions. - Policy Measures and Sustainable Practices
Governments worldwide are implementing policy measures to promote sustainable agriculture practices and combat the effects of climate change on food production. These policies include promoting agroecology, supporting organic farming, and incentivizing the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices. By integrating sustainable practices like crop diversification, conservation tillage, and agroforestry, farmers can enhance ecosystem resilience, soil health, and crop productivity while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The amalgamation of technological innovations, policy interventions, and sustainable agricultural practices is crucial in fostering climate-resilient agriculture and ensuring food security in the face of ongoing climate change challenges globally.
Economic Implications
As I delve into the economic implications of climate change on global agriculture, it’s crucial to consider the significant costs incurred by farmers and nations worldwide due to environmental challenges.
Cost to Farmers and Nations
In analyzing the cost to farmers and nations, it’s evident that climate change poses a substantial financial burden. Farmers face increased expenses in adopting climate-resilient practices, such as investing in new crop varieties and irrigation systems to cope with changing weather patterns. Additionally, crop losses resulting from extreme weather events can lead to reduced income for farmers, impacting agricultural productivity at a national level. The need for extensive insurance coverage and disaster relief further escalates the economic strain on both farmers and governments. These costs not only affect the agricultural sector but also have ripple effects on food security, employment, and overall economic stability.
Potential for Agricultural Investment
Considering the economic challenges brought about by climate change, there is a growing recognition of the potential for agricultural investment to mitigate its impact. Investing in research and development of climate-smart technologies and practices can enhance agricultural resilience and productivity. Governments and private sector entities are exploring opportunities to fund innovative solutions such as precision agriculture, agroforestry, and sustainable land management. By redirecting investments towards climate adaptation strategies, there is a significant potential to not only offset the economic losses incurred by farmers but also foster sustainable agricultural development in the face of environmental uncertainties.